

Powering nearly 30% of all websites on the Internet, WordPress without any shadow of a doubt is the undisputed king of CMS arena today. Initially started as a blogging-focused platform, it has seen a number of noteworthy changes and improvements over the past years since its inception in 2003 and is now a full-fledged eCommerce platform, powering over 42% of all online stores according to statistics provided by the BuiltWith.
However, despite getting so many big updates, there's still one area where WordPress needs significant improvements: its word processor-like backend content editor. Well, the wait is over as the WordPress core team is working hard to completely modernize, streamline, and simplify the entire content creation process with the project Gutenberg – the future editor of WordPress aimed at revolutionizing the publishing experience for both new and casual users.
If you have ever used WordPress for a while, you’ll find the default editor simple, easy-to-use and intuitive. Not only it allows you to create posts, pages, and other types of content quickly and easily, but also it offers two modes for editing content: Visual and Text. While the Visual mode gives you a rough idea of how your content will look like after publishing and includes several buttons to help you format your content, the Text mode, on the other hand, shows you the raw HTML code and utilizes Quicktags API for formatting.
So here a genuine question arises as to what is the need of new Gutenberg WordPress editor if the standard editor is so powerful and easy to use? Well, if you’re an avid WordPress user, you might have noticed that the current editor lacks the functionality of creating rich and beautiful post layouts. This compels users to embrace a third-party plug-in or page builder offering a better or similar content editing experience that they’re looking for.
In fact, the dramatic growth and adoption of various page builders over the past few years made the WordPress core team realize that the users are now looking for a comprehensive, drag-and-drop editing experience similar to what other modern website building platform such as Medium, Wix, and Squarespace are offering to their users. That is why the team is now working on the Gutenberg Editor to provide users the simplest and easiest way to produce rich content – absolutely without using any third party page builder plug-in or tool.
Let’s get acquainted with the brand-new Gutenberg WordPress Editor and learn how it works!
To put it simply, Gutenberg is a new block-based, page builder-like content editor designed to make the addition of rich content to WordPress as simple and enjoyable as possible for users and replace the current TinyMCE editor in the upcoming release of WordPress (probably version 5.0). Named after Johannes Gutenberg who invented a mechanical movable type printing press about 500 years ago, the new editor introduces an entirely new block-based editing approach to content, unlike the current editor that doesn’t even take article structure into account.
Blocks unify all the formatting elements that we currently use to style the content of a post or page in WordPress - like shortcodes, widgets, theme options, custom post types, meta-boxes, etc. – into a single, searchable content editing interface. A block can be pretty much anything, like regular text, a quote, a button, an image or anything that a developer is able to develop as a block. Thus, replacing the single edit window of the current editor with several individual blocks which you can customize and rearrange to fit your content requirements, the new Gutenberg Editor empowers you to build more complex post designs without touching the HTML and CSS code.
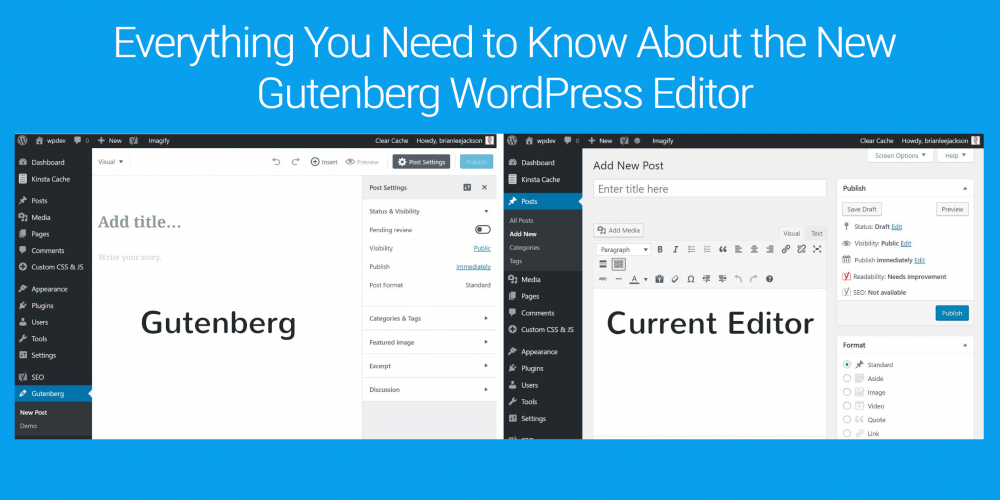
To sum it up: pretty much. If you’ve ever used the Medium platform, you’ll find the new editor has a very similar look and feel to the Medium editor: minimal design, a lot of white space and a full focus on the content creation process. If you’re wondering how the new WordPress Gutenberg editor looks like, here is the snapshot:
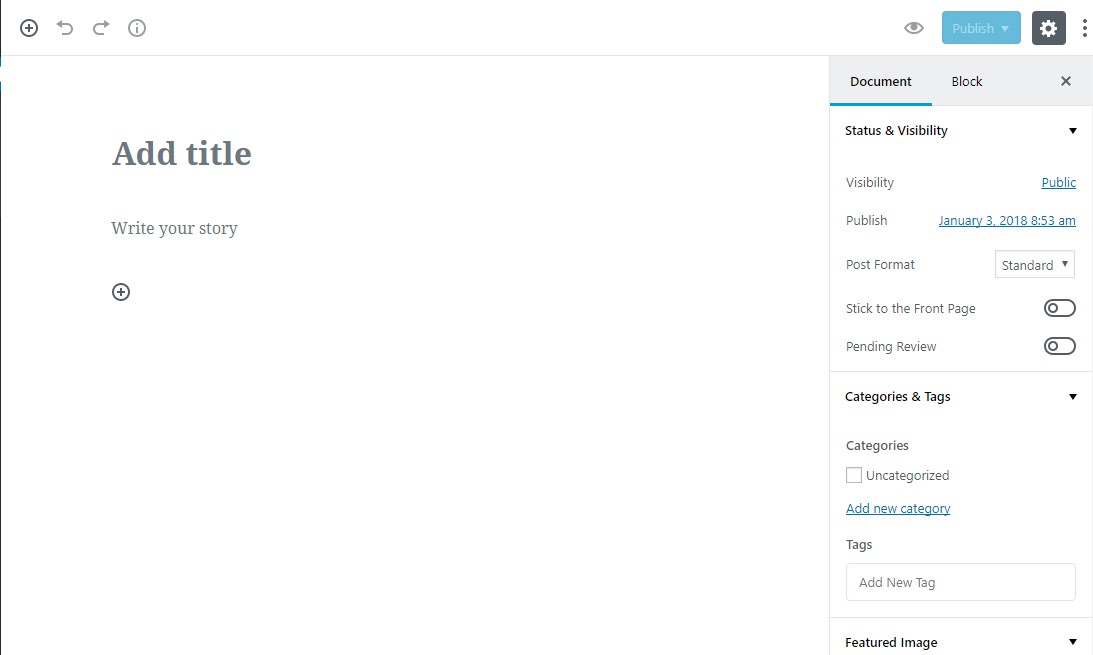
However, as you can see, it looks quite different than the current WordPress TinyMCE editor you have been using so far:
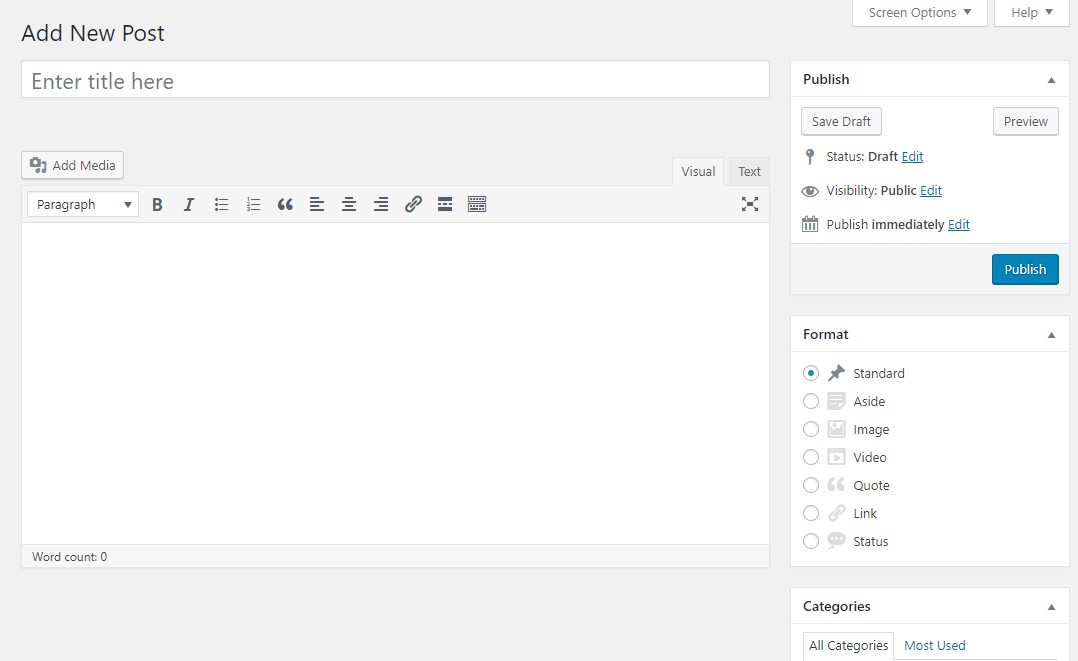
Apart from being visually different from the current WordPress editor, the new Gutenberg editor is several steps ahead in terms of what it offers to users:
Since the inclusion of the Focus plug-in in version 4.1, WordPress has been offering users a distraction-free writing mode. The Gutenberg editor takes it to a whole new level by the use of blocks that eliminate users' need to rely on menu bars, sidebars and other options available for the formatting of content. Everything from the writing to formatting can be handled through the white, minimal edit field. Just click the ‘Post Settings’ button given in the top-right corner and you’ll enter to a truly distraction-free writing environment.
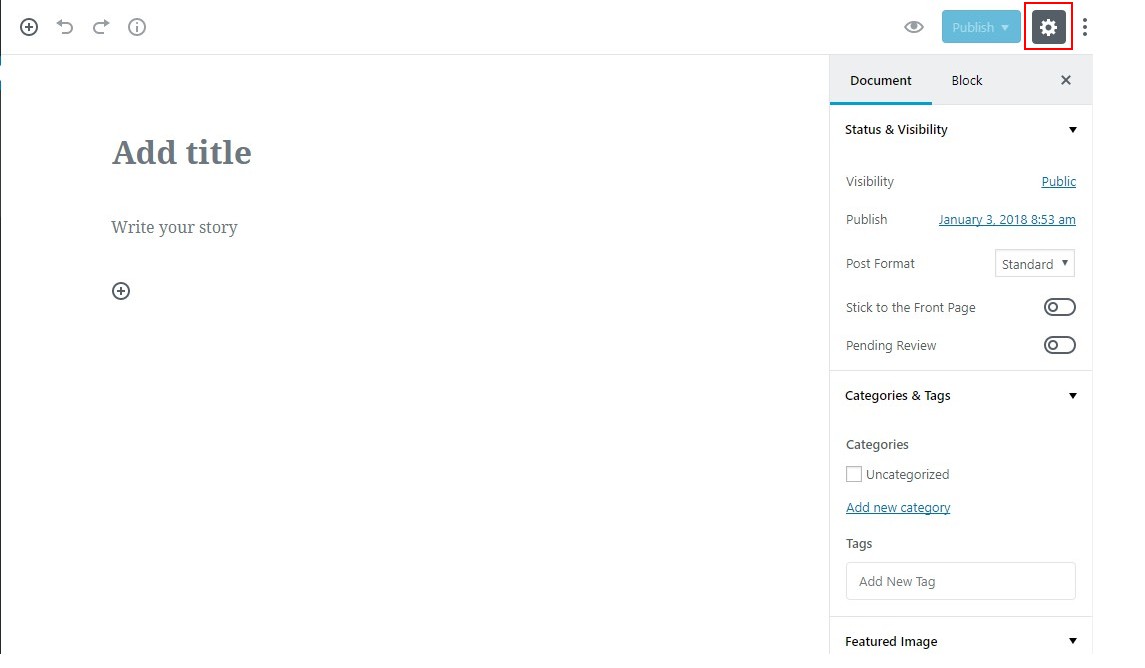
The Gutenberg editor makes the entire process of content creation – including writing, editing, and formatting – a breeze for users. Establishing a unity between the front-end and back-end of your WordPress site, the new editor provides users a better sense of how the content available in the back-end editor will look like on the front end of their website. This is the same issue that third-party page builders have long tried to solve. Adopting this great change, WordPress simply wants to enhance the usability, flexibility, and ease of use of the editor.
So far you were not able to create a rich post layout in WordPress unless you make use of HTML5/CSS3 or build your own custom theme. However, with the inclusion of Gutenberg editor in WordPress, you’ll have the ability to write rich posts effortlessly and seamlessly. For instance, a theme geared towards travel bloggers could develop their own block of Destinations. It might include predefined fields for top sights, popular religious places, and images. Although many of such functionalities can already be accomplished through custom fields and custom post types, a custom block makes writing rich posts a bit easier for users.
Shortcode and Embed Discovery:
Unlike the current WordPress editor, where it is quite difficult to find shortcodes and embeds, Gutenberg makes the discovery of shortcodes and embeds easier for editors. Since everything in Gutenberg is a content block, users just need to type in the shortcode or embed they’re looking for and it will be instantly presented in front of their eyes. Moreover, developers can create content blocks for their unique shortcodes needs, which will eventually facilitate a better code reuse.
According to the official Gutenberg page, the new editor has three planned stages. While the initial phase focuses solely on the content creation, implementation of blocks and inclusion in WordPress 5.0, the subsequent stages are aimed at turning the editor into a full site customization tool. This means in the near future you'll be able to build more complex standalone pages, like landing pages and other important pages, using the Gutenberg. Even if Gutenberg is not able to even compete with page builders in its current form, it will definitely provide a well-defined approach to build complicated pages and replace page builders someday.
Currently, if multiple people are working simultaneously on a post in WordPress, the post locking feature prevents others from accessing and modifying the post. In the new Gutenberg editor, the same feature can be implemented at the block level, allowing two or more people work on different sections of a draft without overwriting each other's stuff. Since commenting is an imperative part of a collaborative workflow, there could be a block for editorial feedback, where users could be able to leave their comments throughout the draft while editing. If collaboration feature is brought to the Gutenberg, you won’t need a third party collaborative editor like Google Docs to draft your articles and leave feedback; it all will be done right from within WordPress.
Currently available as a free plug-in, the Gutenberg Editor is still in beta and therefore it is not advised for use on a live site. Install the Gutenberg plug-in on a testing site like you would any other plug-in and you'll be able to see the Gutenberg link under your every post and page as shown below:
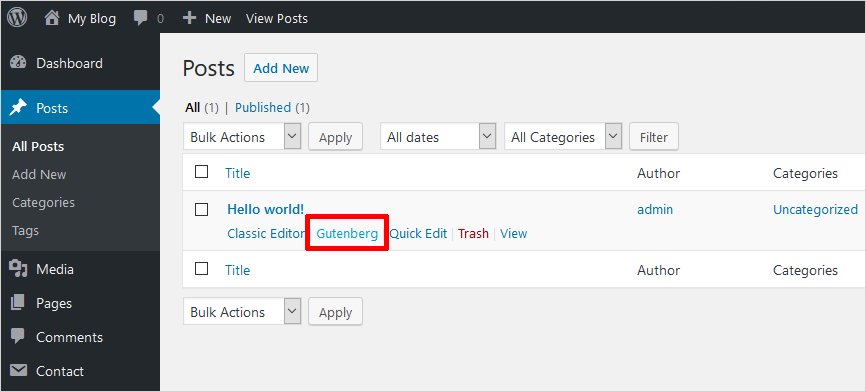
The Gutenberg plug-in being in testing phase doesn’t replace the default WordPress editor, which is really a good thing. However, when you create a new post or page after installation, your site will automatically use the Gutenberg editor. But don't worry as you can still access the default editor by using the drop-down menu which opens up when you click on the Add New button:
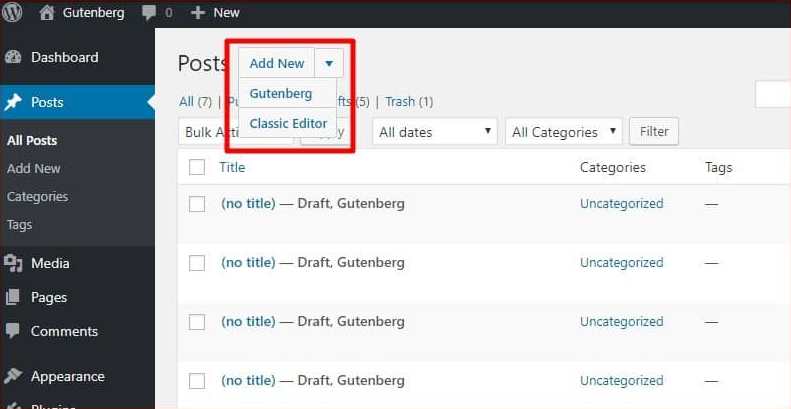
Activating the Gutenberg plug-in on your WordPress site also adds a new ‘Gutenberg’ menu to your Dashboard which contains a Demo and a link to let you create a new post, as shown below:
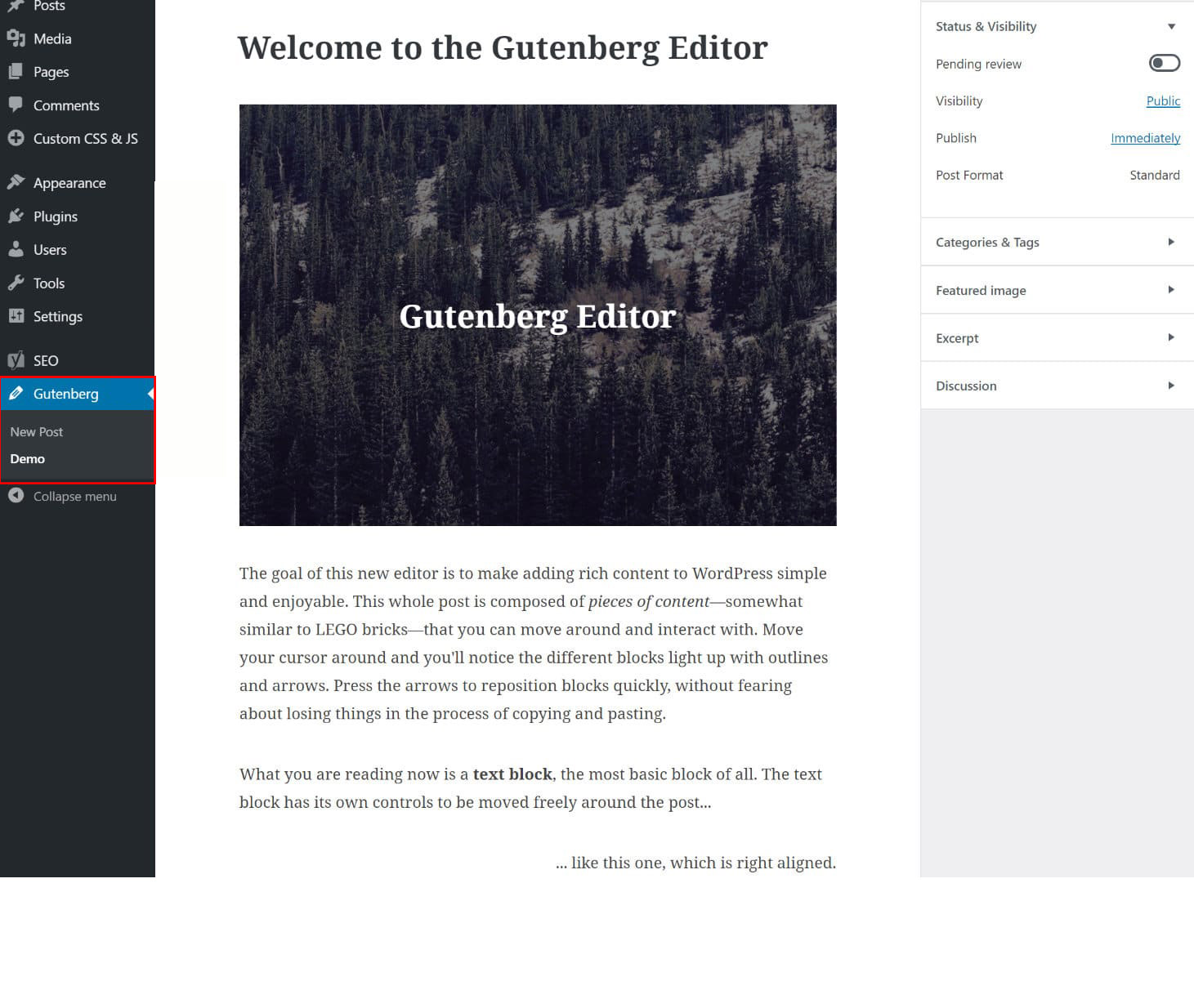
When you create a new post with Gutenberg, here’s what you’ll see:
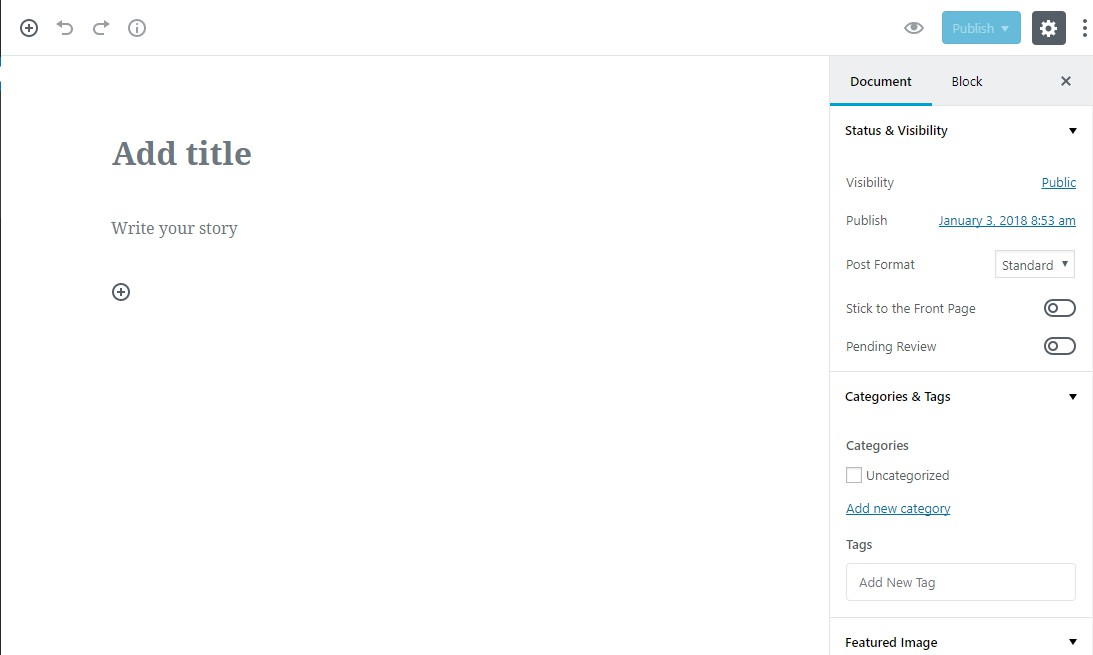
A completely distraction-free writing experience! Isn't it? Before you add any block to your new post, let’s get familiar with what the various areas of the main Gutenberg interface let you do:
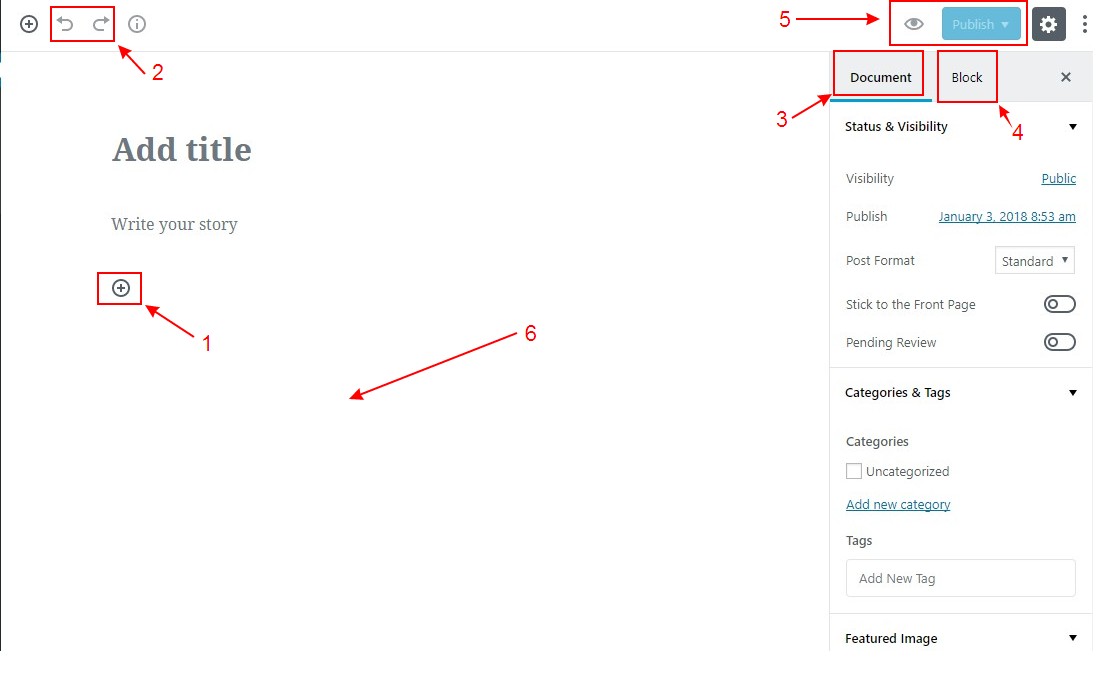
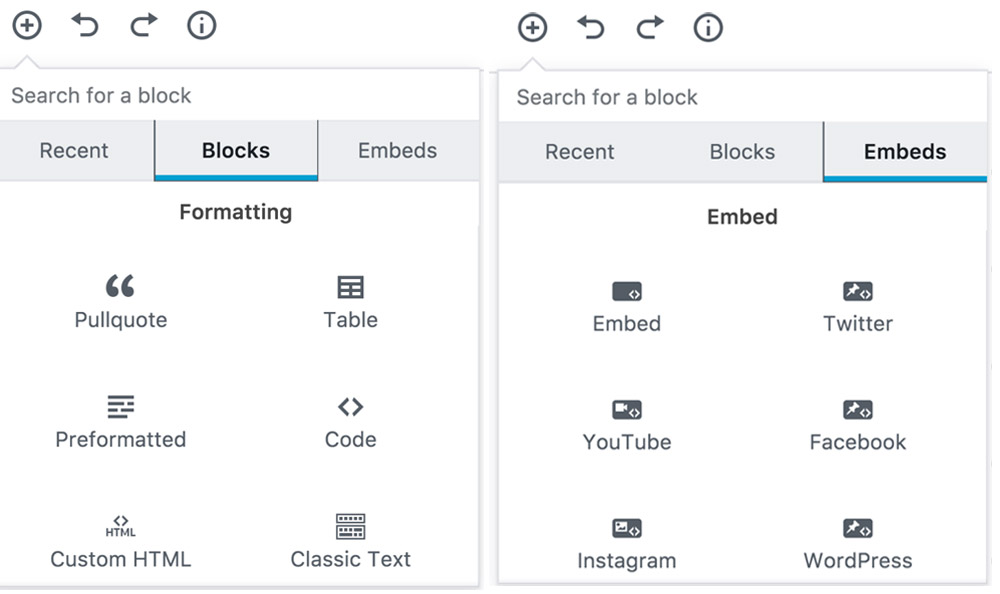
To insert a new block into your post, all you need to do is click the + icon and select the type of block that you want to use in your content. Clicking the + icon actually opens a new window divided into four sections: Recent, Blocks, Embeds and Saved.
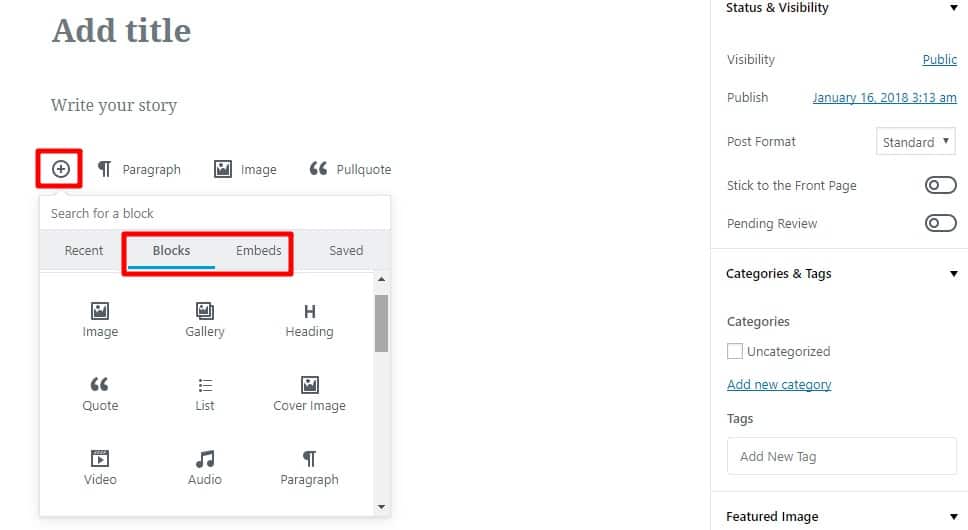
While the Recent and Saved tabs allow you to quickly access your frequently used blocks, Blocks and Embeds tabs let you access all the available blocks. Shown below are all the available blocks using which you can customize the post content and its layout:

And using the Embeds tab, you can embed content from several external sources including but not limited to YouTube, Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram.
You can easily move the blocks up and down with arrows given to the left of each block. As mentioned earlier, you can also delete or change the settings of a particular block with the ‘Block’ option given in the sidebar.
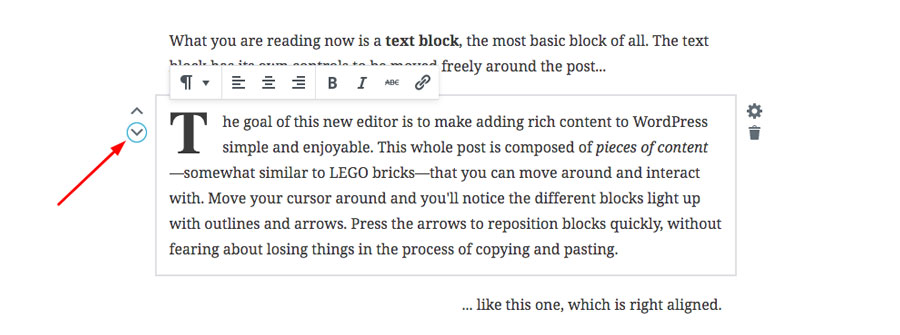
To align a block left, center or right, you can use the ‘Block Alignment’ option given at the bottom of the sidebar. However, you must have already selected the ‘Block’ tab to use the ‘Block Alignment’ option.
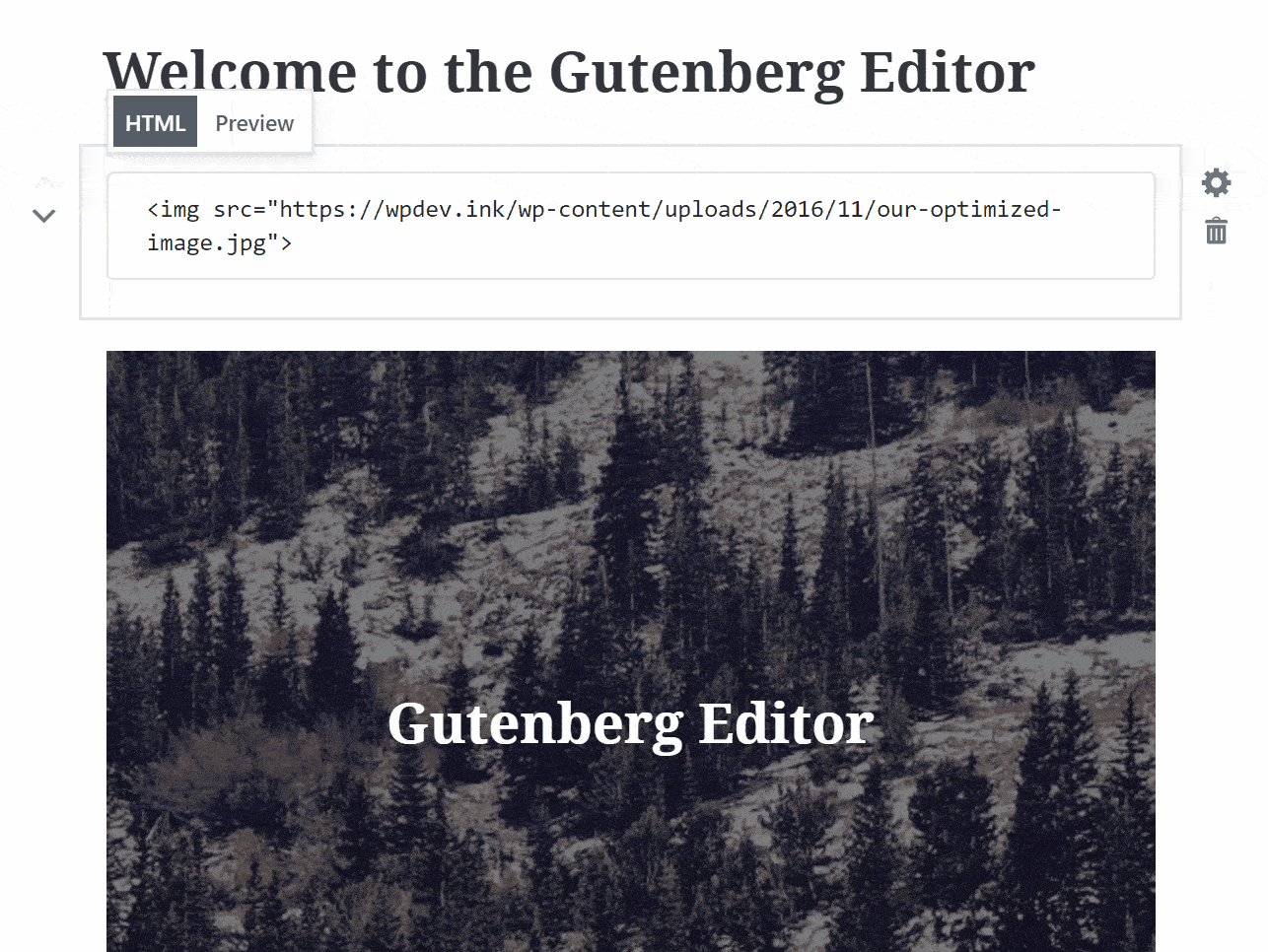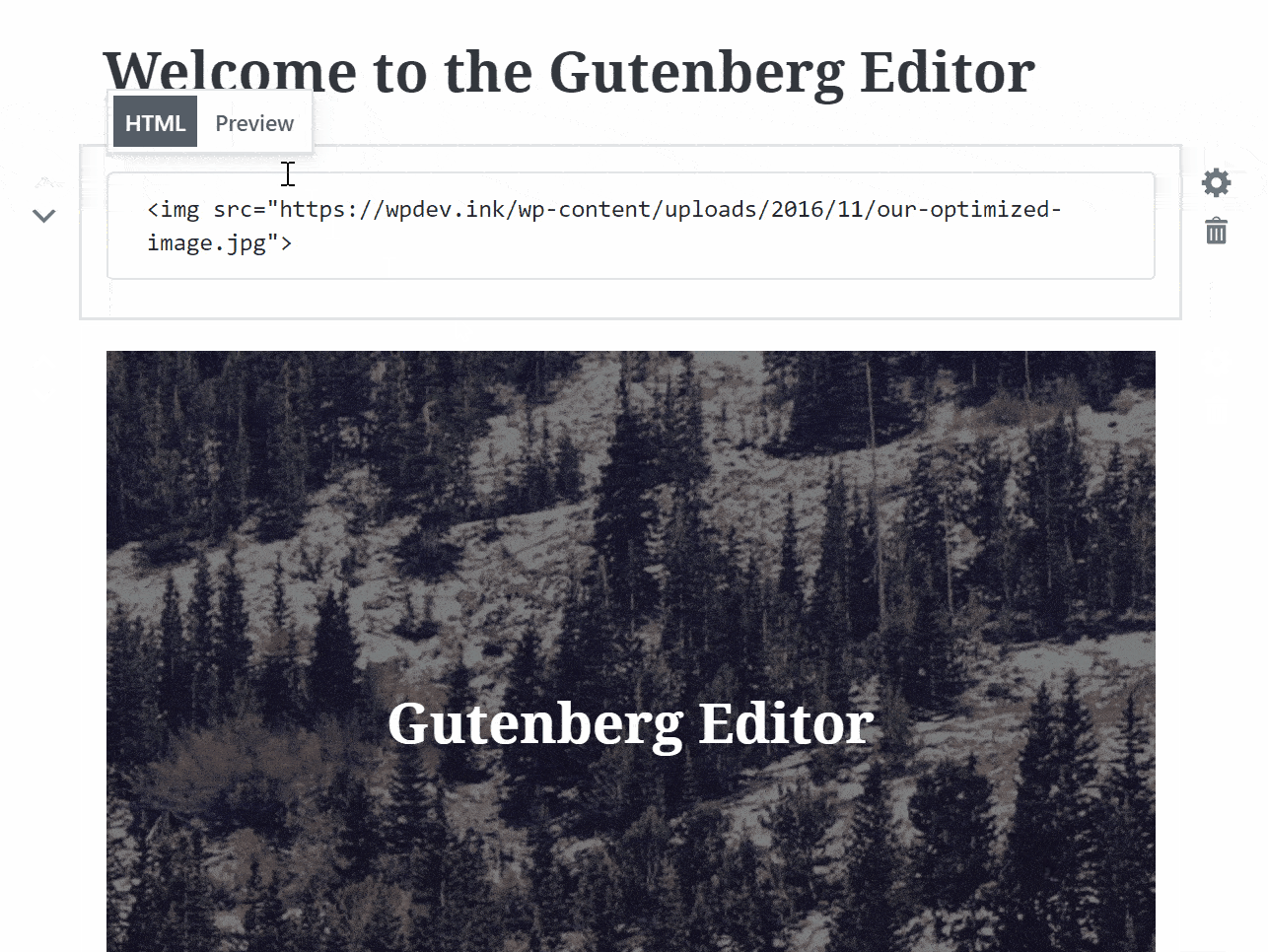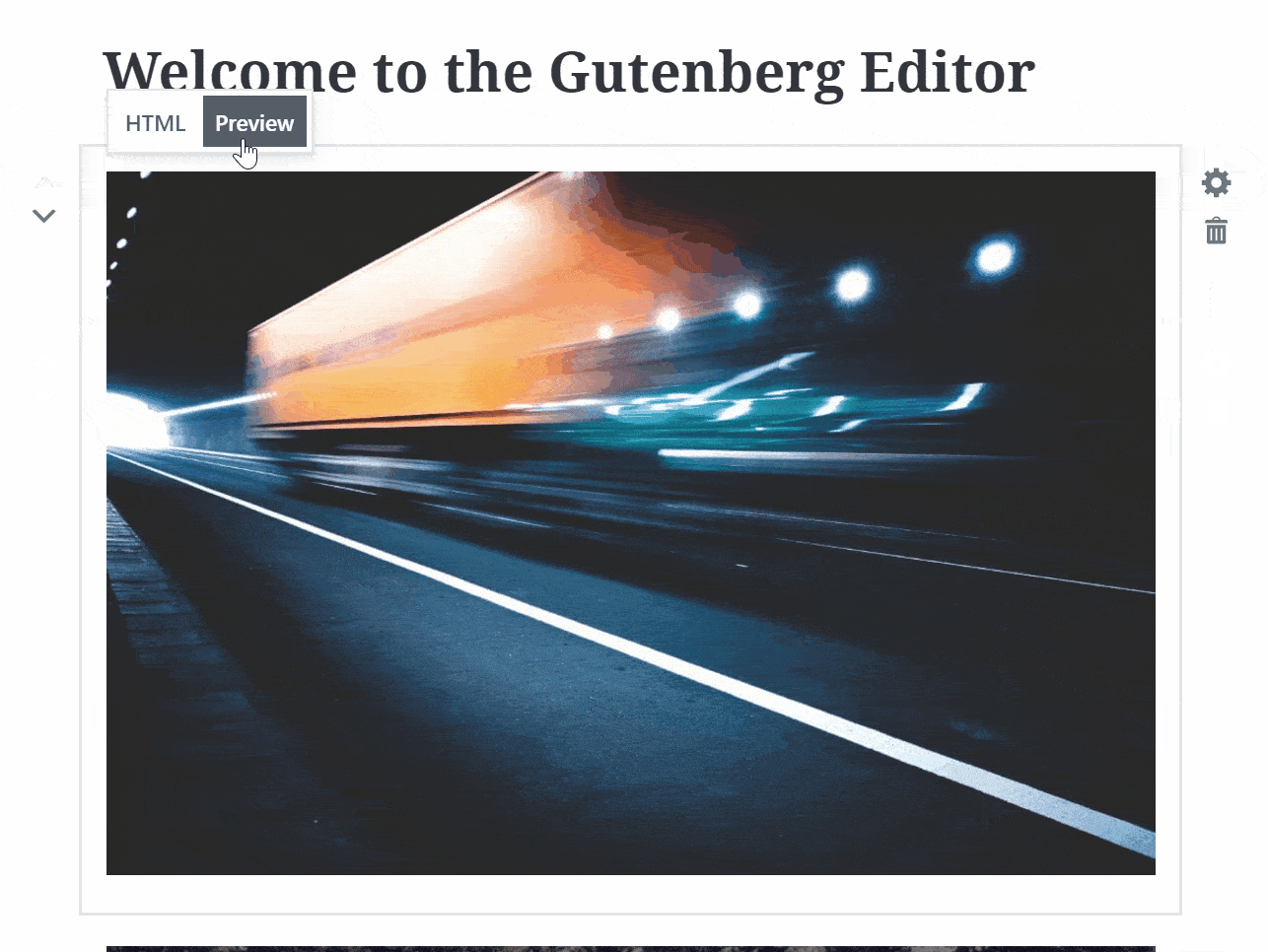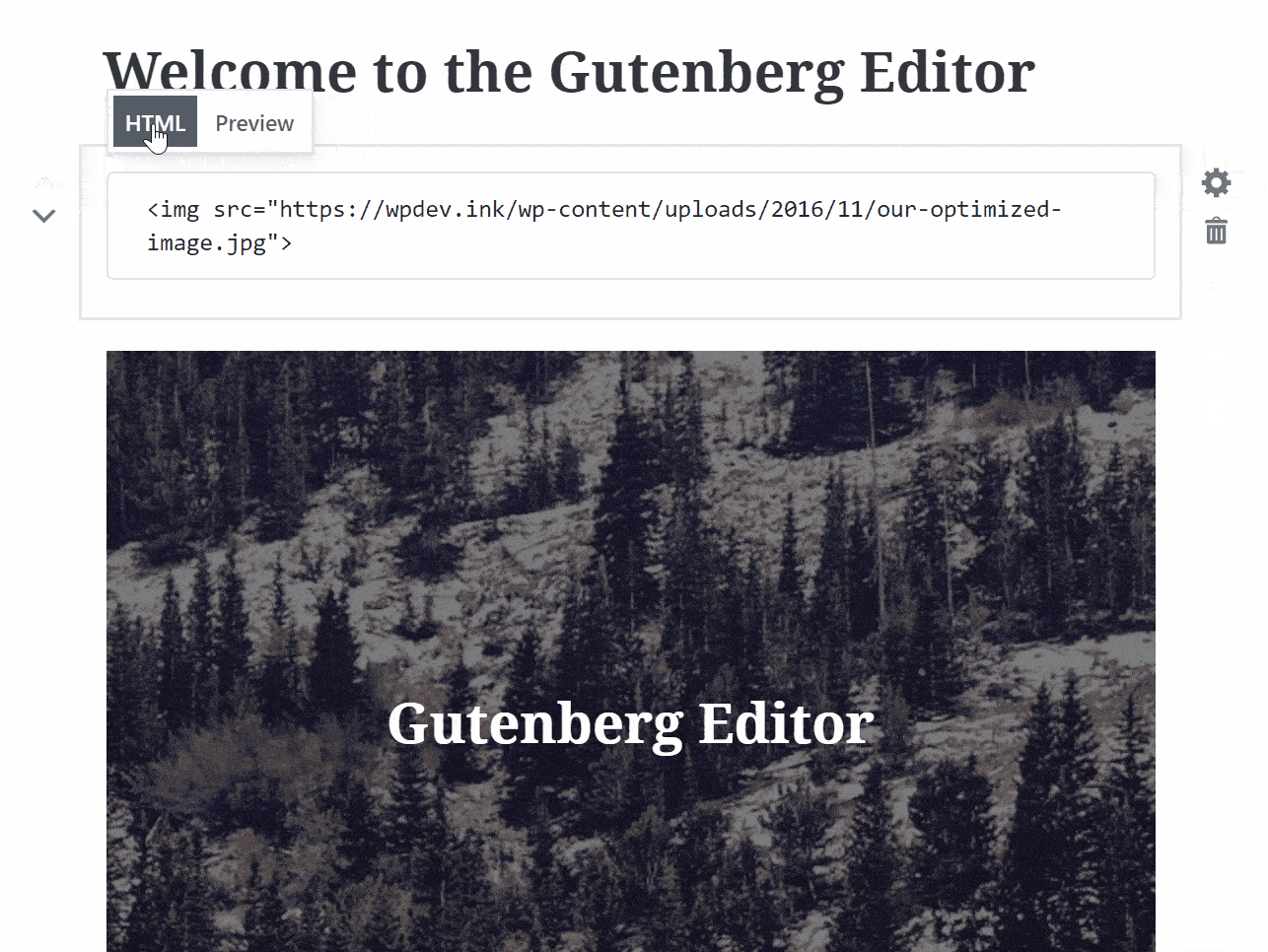
This is actually a pretty cool feature of the Gutenberg which allows you to preview your HTML code from right within the block and save you from switching back and forth between the visual and text editor for the same.
Gutenberg is also packed with an inbuilt option to add simple buttons to your post content. With the new editor, there is no need to rely on HTML code or a third-party plug-in to add the call to actions to your blogs posts.

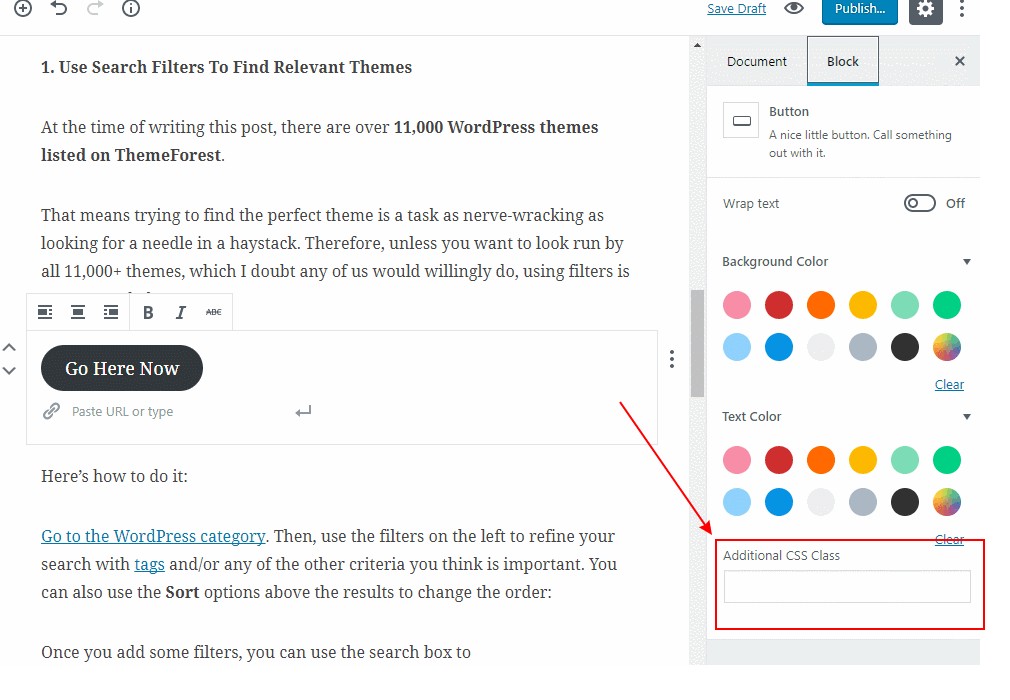
While the most blocks in Gutenberg have an option to add custom CSS styles, this feature proves quite helpful to enhance the default styling of a specific block element.
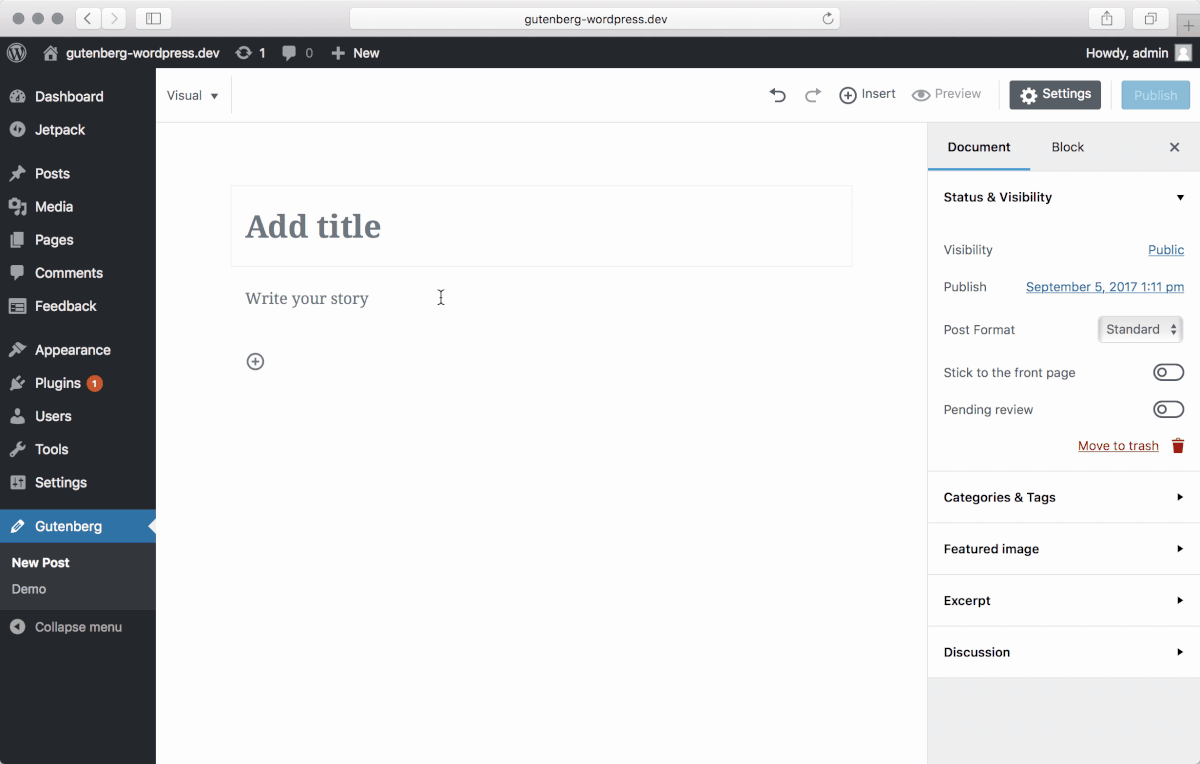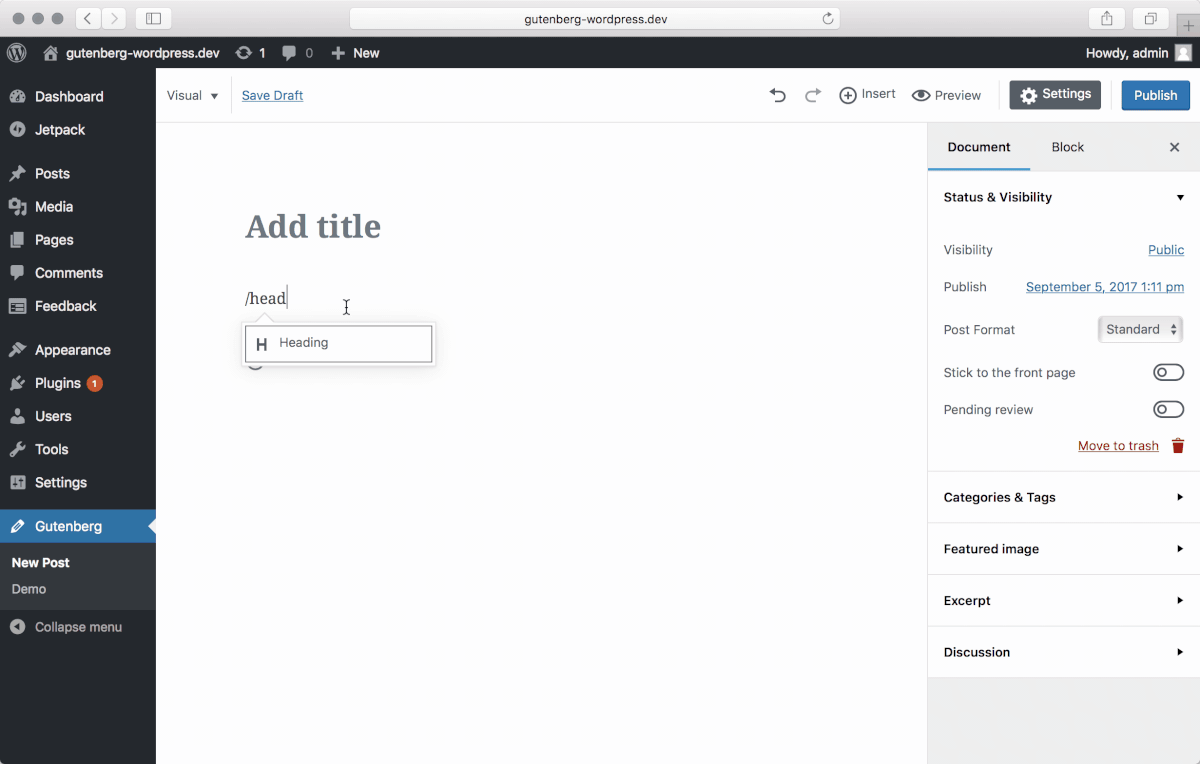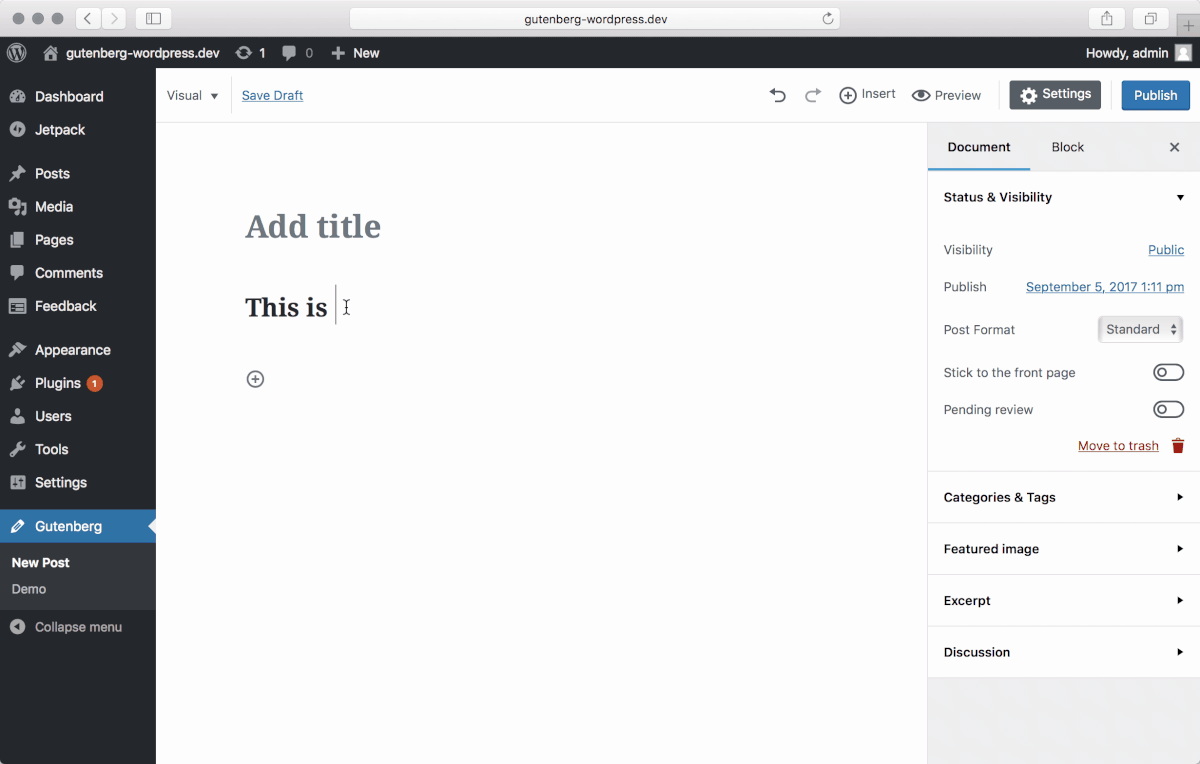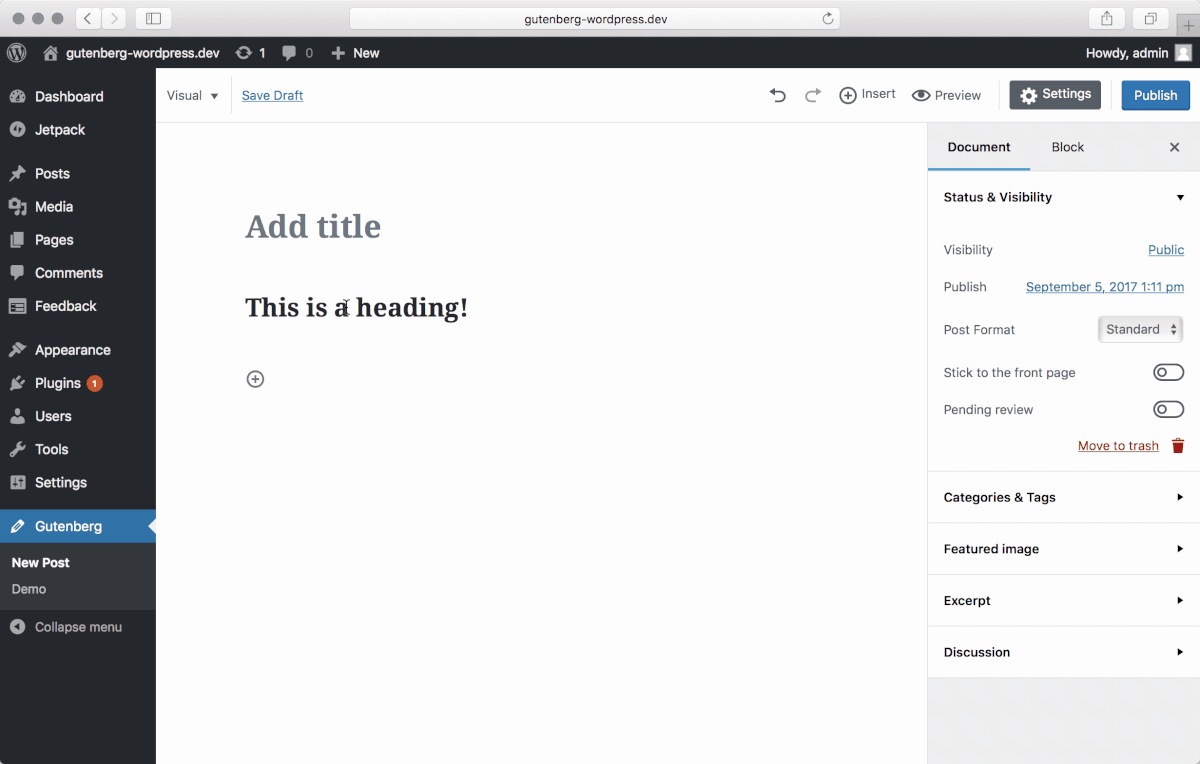
This cool feature facilitates you to use the autocomplete to insert blocks in your posts. For example, if you type heading, it will automatically start inserting a Heading text.
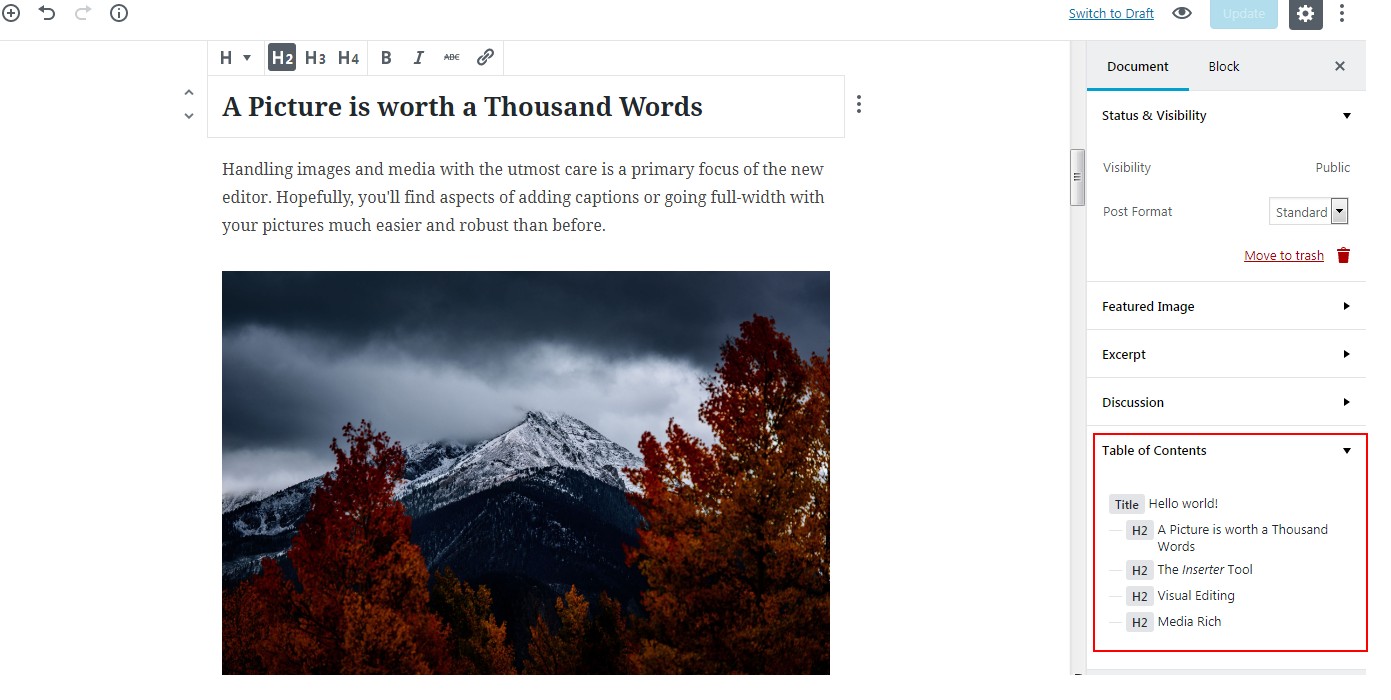
Detecting all the Headings in your posts, Gutenberg displays a Table of Contents in the sidebar. Since all the links in ToCs are clickable, you can jump into any part of your article quickly and freely. This can come in handy in case of long-form content.
Another great feature Gutenberg offers is an HTML Anchor tag, using which you can link directly to the header or a specific section of your post. This is great for sharing as well as showing "jump to" links in search engine results.

As Gutenberg continues to evolve and is gradually getting closer to being merged into the WordPress core, there are a number of valuable resources coming out to help you learn more about the project. Here are just a few of them:
Comments are Closed